Translate
venerdì 12 settembre 2025
# gst: shock waves in classical dust collapse.
mercoledì 9 luglio 2025
# gst: the evasion of tipping; pattern formation near a Turing-fold bifurcation
martedì 4 febbraio 2025
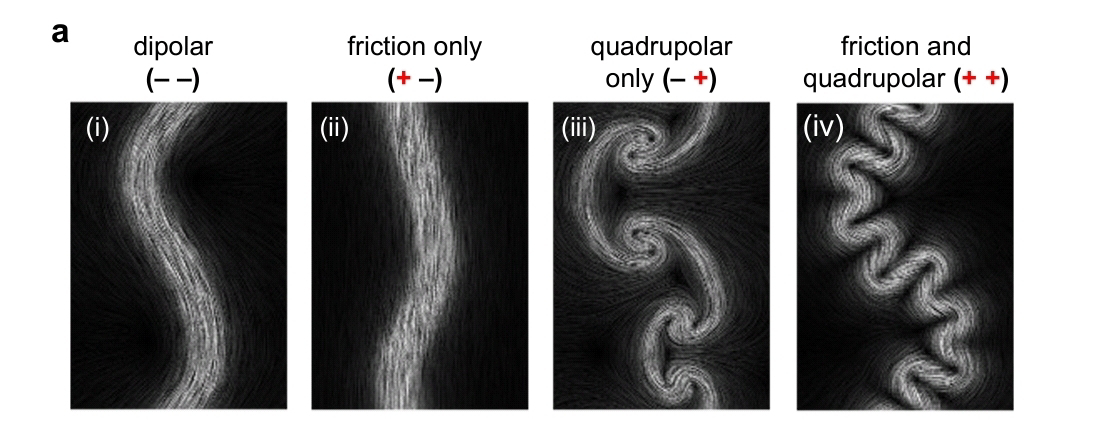
# gst: quadrupolar stress drives collapse of nematic order on frictional substrates.
martedì 30 luglio 2024
# gst: collapse of a toroidal bubble inducing shock waves
lunedì 5 luglio 2021
# gst: apropos of (multitudes) of transitional droplets, when a liquid film collapses in a foam ...
mercoledì 19 agosto 2020
# gst: the role of surface tension during the collapse of a viscous bubble
lunedì 2 settembre 2019
# geo gst: even small flank failures can cause large tsunamis
<< Volcanogenic tsunamis are one of the deadliest volcanic phenomena. >>
<< Small flank failures causing large tsunamis represent a vastly underappreciated geohazards-current tsunami monitoring systems do not monitor for this kind of volcanic activity, instead focusing on large earthquakes or proxies related to unusual increases in magma intrusion. >>
<< This collapse was captured in unprecedented detail by satellite remote sensing, providing an opportunity to understand the collapse of the volcano (Anak Krakatau volcano, Indonesia) in a way that has not previously been possible at any volcanic island in the world. >>
Reconstructing the Anak Krakatau flank collapse that caused the December 2018 Indonesian tsunami. Geological Society of America. Aug 30, 2019. https://m.phys.org/news/2019-08-reconstructing-anak-krakatau-flank-collapse.html
<< the volume of material initially lost from the volcano flank failure (..) was relatively small (~0.1 km3) compared to the overall changes observed during the entire eruption, but it was nonetheless able to generate rapid tsunami waves with devastating impacts. The flank failure also changed the eruption style and the upper volcanic plumbing system, with the subsequent explosive eruptions destroying the summit and then partially rebuilding the lost flank. >>
Rebecca Williams, Pete Rowley, Matthew C. Garthwaite. Reconstructing the Anak Krakatau flank collapse that caused the December 2018 Indonesian tsunami. Geology. doi.org/10.1130/G46517.1. Aug 30, 2019. https://pubs.geoscienceworld.org/gsa/geology/article-abstract/573356/reconstructing-the-anak-krakatau-flank-collapse