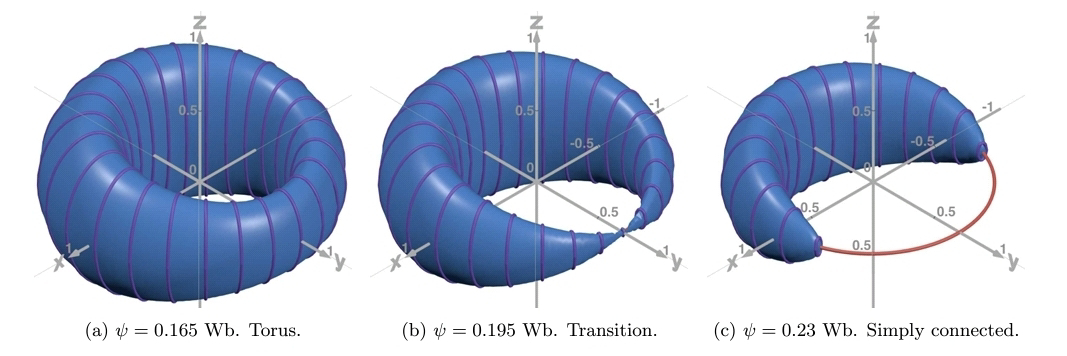
<< ️(AA) address the existence, stability, and dynamics of single-ring and multi-ring vorticity-carrying necklace solitons under the action of the Kerr nonlinearity and a Bessel-lattice potential modulated in the azimuthal direction. The model may be realized in the spatial domain for bulk optical waveguides, the spatiotemporal domain for optical cavities, and for effectively two-dimensional Bose-Einstein condensates. The setup supports single- and multi-ring necklace vortex patterns, including monopoles, dipoles, tripoles, quadrupoles, pentapoles, sextupoles, octupoles, and 12-poles. >>
<< ️In contrast with the inherent instability of conventional vortex beams with high topological charges (winding numbers), vortex necklace-shaped solitons with large winding numbers are found to be stable in the present setup. In particular, octupoles exhibit stable breathing dynamics, and 12-pole necklaces with high winding numbers may be stable. >>
<< ️These (AA) findings provide a new way for generating stable vortex necklaces, offering a vast potential for manipulations of complex spatiotemporal light fields. >>
Ruolan Zhao, Jing Chen, Boris A. Malomed, et al. Multi-ring necklace vortex solitons in Kerr nonlinear media with azimuthally modulated Bessel potentials. arXiv: 2602.18703v1 [physics.optics]. Feb 21, 2026.
Also: vortex, soliton, transition, in https://www.inkgmr.net/kwrds.html
Keywords: gst, vortex, solitons, vortex necklace-shaped solitons, single-ring vorticity, multi-ring vorticity, stable vortex necklace, transitions.