<< ️(AA) experimentally investigate the dynamics of synthetic active particles composed of gravitationally bouncing, superwalking droplets confined within an annular fluid bath. >>
<< ️Driven by a topologically pumping dual-frequency waveform, the droplets exhibit alternating active (walking) and dormant (bouncing) phases, producing intermittent azimuthal motion. Tracking individual droplets reveals pseudolaminar chaotic dynamics in the time series of particle's angular position, characterized by laminar plateaus that are interrupted by short irregular bursts of activity. >>
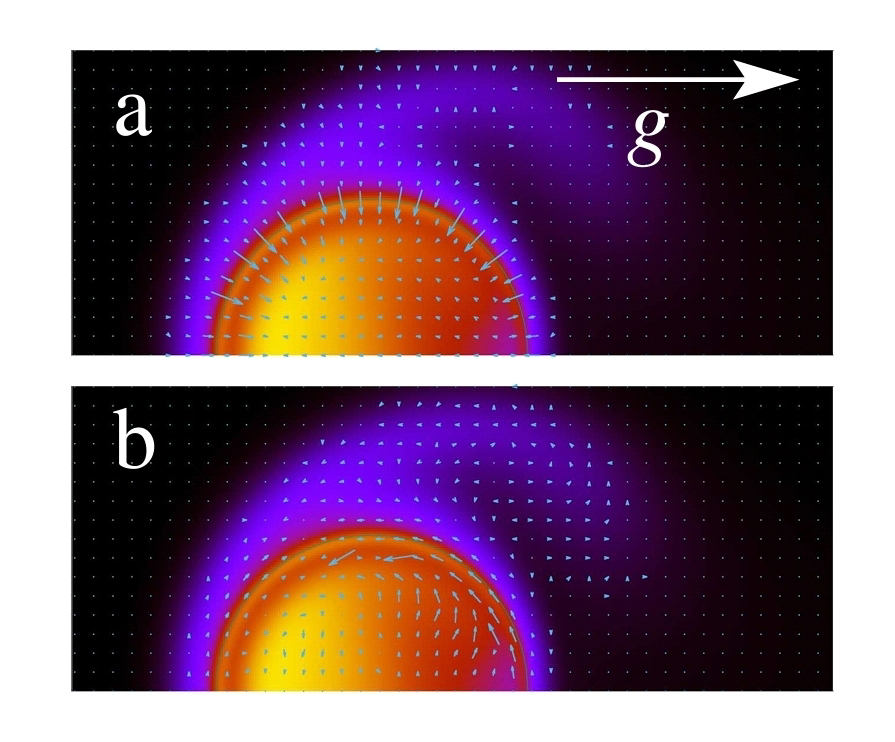
<< ️Increasing the driving amplitude induces a qualitative change in the active particle's intermittent dynamics, arising from a symmetry-breaking transition in its Faraday-wave field environment: continuous SO(2)-symmetric "channelling" waves give way to discrete "trapping" patterns. >>
<< ️These findings demonstrate how environmental symmetry and spatiotemporal structure modulate motility and intermittency in synthetic active matter. >>
Rudra Sekhri, Rahil N. Valani, Tapio Simula. Intermittent Motility of a Synthetic Active Particle in Changing Environments. arXiv: 2512.16135v1 [physics.flu-dyn]. Dec 18, 2025.
Also: drop, droplet, droploid, intermittency, behav, in https://www.inkgmr.net/kwrds.html
Keywords: gst, active matter, drops, droplets, droploids, intermittency, behavior, active walking phase, dormant bouncing phase, trapping patterns.