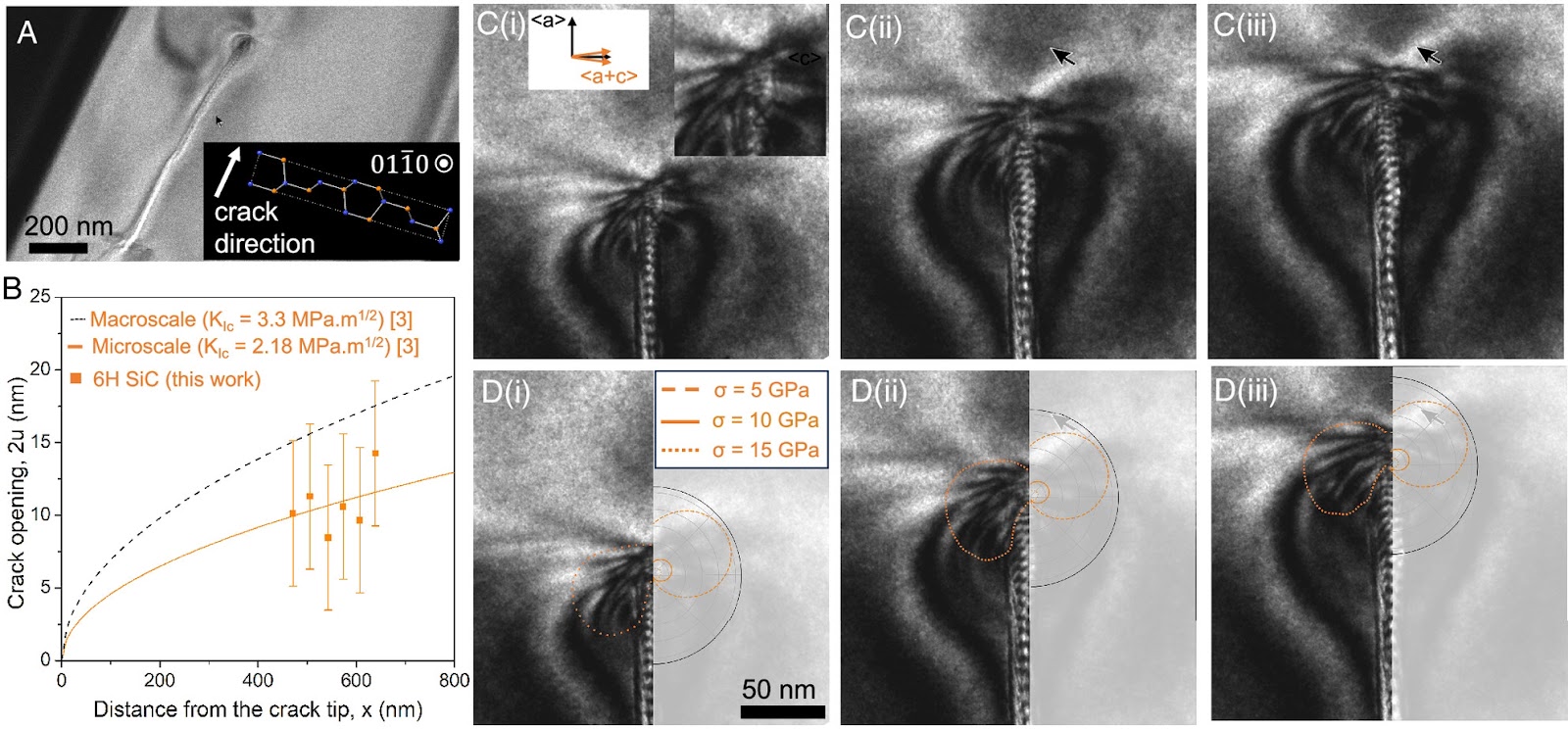
AA << successfully imaged the snapping of individual atomic bonds in a one-atom-thick sheet of rhenium disulfide ( ReS2) using scanning transmission electron microscopy. (STEM) >>
<< Because of its unusual chemistry, Re forms a 2D lattice with "lanes" that guide cracks, allowing the cracks to propagate with ease. The heavy element also efficiently deflects electrons, providing the signal needed to gain clear images. The study is a remarkable example of how a specific material can provide insight into the universal behavior of matter. >>
<< Because of its strong scattering, ReS2 provides an ideal target for STEM. (Interestingly, tungsten, the periodic-table neighbor of Re, has just one fewer proton and is routinely used in electron microscopy to stain viruses and bacterial flagella.) >>
<< By measuring the deformation of the lattice around the crack, the team showed that the tearing stresses were concentrated around the crack tip. The stresses then decayed as the inverse square root of the distance from the tip, a finding that matches predictions for macroscopic materials. Using these measurements, the team defined a stress intensity threshold for cracks to propagate. >>
<< The images taken by Huang and colleagues used seconds-long exposure times, meaning they could only follow the propagation of the slowest crack (those that moved at a few angstroms per second). There is much interest in how faster cracks behave, as these cracks are subject to instabilities, meaning they can deviate from a straight line or form branches, for example. To observe faster cracks, future experiments could use reduced exposure times. >>
Itamar Kolvin. Atomic Imaging of Cracks. Physics 13, 193. Dec 9, 2020.
Lingli Huang, Fangyuan Zheng, et al. In Situ Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy Observations of Fracture at the Atomic Scale. Phys. Rev. Lett. 125, 246102. Dec 9, 2020.
Also
(+) the intriguing dynamics of a crack. Nov 7, 2017.
(+) multiple cracks, simultaneously ... Oct 23, 2016.
(+) onda criptica. May 22, 2005 (quasi-stochastic poetry)
(+) keyword "fracture" in FonT