Translate
giovedì 10 febbraio 2022
# gst: liquid–liquid phase transition, the two forms of liquid water (mixed with the natural antifreeze trehalose)
mercoledì 5 febbraio 2020
# chem: more on the weirdness of water, "T" and "non-T" Tetrahedral arrangements
sabato 1 luglio 2017
# s-chem: more on the anomalous properties of water
<< Most of us know that water is essential for our existence on planet Earth. It is less well-known that water has many strange or anomalous properties and behaves very differently from all other liquids >>
<< Some examples are the melting point, the density, the heat capacity, and all-in-all there are more than 70 properties of water that differ from most liquids >>
<< These anomalous properties of water are a prerequisite for life as we know it >>
<< "The new remarkable property is that we find that water can exist as two different liquids at low temperatures where ice crystallization is slow" >> Anders Nilsson.
Water exists as two different liquids. June 26, 2017.
https://m.phys.org/news/2017-06-liquids.html
Fivos Perakisa, Katrin Amann-Winkela, et al. Diffusive dynamics during the high-to-low density transition in amorphous ice. PNAS 2017 doi: 10.1073/pnas.1705303114.
lunedì 30 dicembre 2024
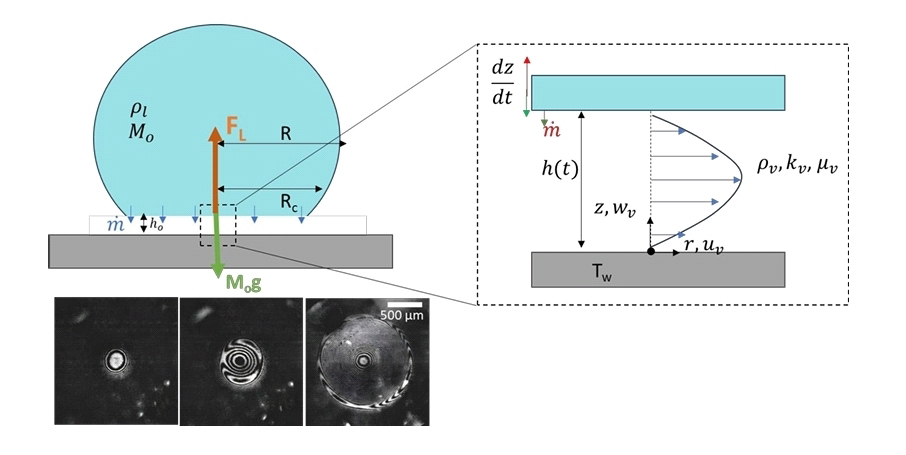
# gst: nascent water waves induced by the impulsive motion of a solid wall; an unsteady hydraulic jump theory
sabato 19 agosto 2017
# phyto: feel sounds to spot water
AA << used the model plant Pisum sativum to investigate the mechanism by which roots sense and locate water >>
AA << found that roots were able to locate a water source by sensing the vibrations generated by water moving inside pipes, even in the absence of substrate moisture. When both moisture and acoustic cues were available, roots preferentially used moisture in the soil over acoustic vibrations, suggesting that acoustic gradients enable roots to broadly detect a water source at a distance, while moisture gradients help them to reach their target more accurately >>
AA << results also showed that the presence of noise affected the abilities of roots to perceive and respond correctly to the surrounding soundscape >>
Monica Gagliano, Mavra Grimonprez, et al. Tuned in: plant roots use sound to locate water. Oecologia. Volume 184, Issue 1, pp 151–160. May 2017
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00442-017-3862-z
sabato 16 aprile 2016
# s-astro: old, very old water
<< As much as half of all the water on Earth may have come from that interstellar gas according to astrophysicists ’ calculations. That means the same liquid we drink and that fills the oceans may be millions of years older than the solar system itself. >>
Nicholas St. Fleur. The Water in Your Glass Might Be OlderThan the Sun. April 15, 2016
http://www.nytimes.com/2016/04/16/science/the-water-in-your-glass-might-be-older-than-the-sun.html
L. Ilsedore Cleeves , Edwin A. Bergin , et al. The ancient heritage of water ice in the solar system. Science 26 Sep 2014: Vol. 345, Issue 6204, pp. 1590-1593 DOI: 10.1126/science.1258055
sabato 16 febbraio 2019
# qubit: an energy control approach to build quantum computers: quickly jump two rungs at a time without spilling any water from the glass
<< Dr. Sergey Danilin, (..) describes quantum control-the process of using chips like transmons to build quantum computers-by extending the "climbing a ladder" analogy. "To get a useful quantum system, you need to imagine climbing a ladder while holding a glass of water-it works if one does it smoothly, but if you do it too fast, the water spills. Certainly, this requires a special skill." (..) in the quantum world, the trick for climbing the ladder quickly without spilling any water is by carefully jumping two rungs at a time. >>
Life on the edge in the quantum world. Aalto University. Feb 8, 2019
https://m.phys.org/news/2019-02-life-edge-quantum-world.html
Antti Vepsalainen, Sergey Danilin, Gheorghe Sorin Paraoanu. Superadiabatic population transfer in a three-level superconducting circuit. Science Advances Feb 8, 2019:
Vol. 5, no. 2, eaau5999
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aau5999
http://advances.sciencemag.org/content/5/2/eaau5999
Also
mercoledì 10 maggio 2023
# gst: to find a separation between plunging and spilling wave breakers
martedì 4 ottobre 2016
# s-gst: about internal tides
<< In certain parts of the ocean, towering, slow-motion rollercoasters called internal tides trundle along for miles, rising and falling for hundreds of feet in the ocean's interior while making barely a ripple at the surface >>
<< Internal tides are generated in part by differences in water density, and created along continental shelf breaks, where a shallow seafloor suddenly drops off like a cliff, creating a setting where lighter water meets denser seas. In such regions, tides on the surface produce oscillating, vertical currents, which in turn generate waves below the surface, at the interface between warmer, shallow water , and colder, deeper water >>
<< Now for the first time [AA] have accurately simulated the motion of internal tides along a shelf break called the Middle Atlantic Bight ... >>
Jennifer Chu. Researchers find explanation for interacting giant, hidden ocean waves. Sept. 28, 2016.
http://phys.org/news/2016-09-explanation-interacting-giant-hidden-ocean.html
Samuel M. Kelly, Pierre F. J. Lermusiaux. Internal-tide interactions with the Gulf Stream and Middle Atlantic Bight shelfbreak front. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans. Volume 121, Issue 8 Aug. 2016 Pages 6271–6294 DOI:10.1002/2016JC011639
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/2016JC011639/abstract
lunedì 25 novembre 2024
# gst: apropos of dances, drops that dance following snake- and ouroboros-shaped trajectories on lubricated surfaces.
giovedì 10 settembre 2020
# gst: the dance (swimming and sinking behavior) of pelagic snails
giovedì 10 ottobre 2024
# gst: apropos of breaking mechanisms, crack of a floating particle raft caused by waves.
martedì 2 settembre 2025
# gst: dynamics and frictional dissipation for treading slowly in a puddle.
giovedì 22 agosto 2024
# gst: spontaneous bouncing, trampolining, and hovering behaviors of a levitating water droplet without constraints.
mercoledì 5 maggio 2021
# gst: when and how a levitating droplet sings (as a pipe)
giovedì 23 febbraio 2023
# gst: hidden complexity during the twinkle of a shrinking droplet
venerdì 14 febbraio 2025
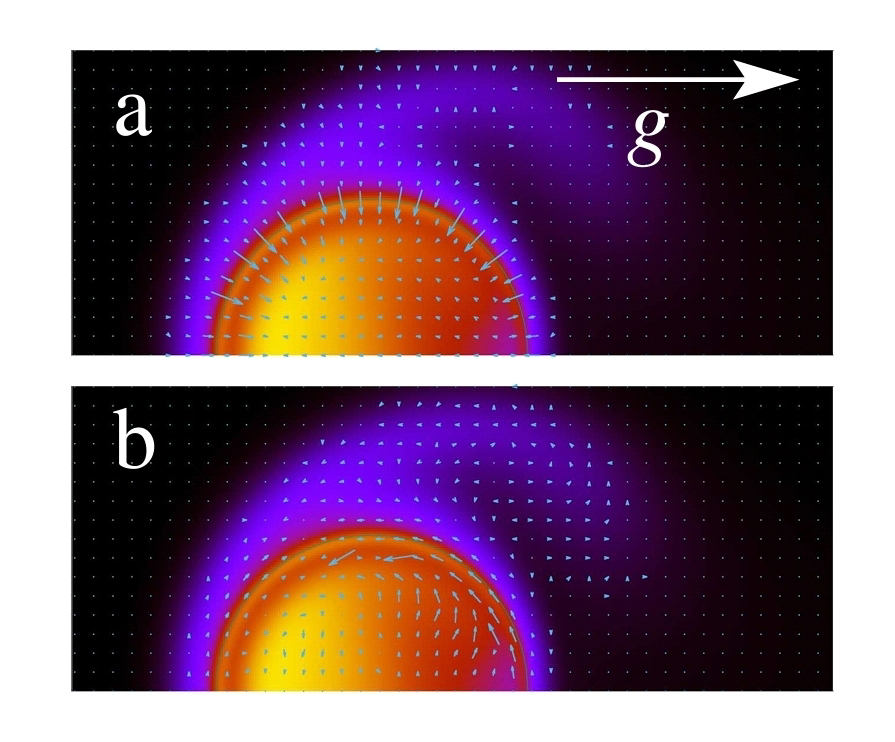
# gst: rise and fall of a multicomponent droplet in a surrounding fluid along a bumpy path.
mercoledì 7 ottobre 2020
# astro: the turbulent history of Ryugu
lunedì 6 maggio 2019
# gst art: an image of chaotic hydrodynamics, by "Leo"
<< One of the first to visualize these flows was scientist, artist, and engineer Leonardo da Vinci, who combined keen observational skills with unparalleled artistic talent to catalog turbulent flow phenomena. Back in 1509, Leonardo was not merely drawing pictures. He was attempting to capture the essence of nature through systematic observation and description. In this figure, https://cdn.arstechnica.net/wp-content/uploads/2018/10/daVinciWake.png we see one of his studies of wake turbulence, the development of a region of chaotic flow as water streams past an obstacle. >>
Lee Phillips. Turbulence, the oldest unsolved problem in physics. The flow of water through a pipe is still in many ways an unsolved problem. Oct 10, 2018.
https://arstechnica.com/science/2018/10/turbulence-the-oldest-unsolved-problem-in-physics/
domenica 9 dicembre 2018
# gst: fingerprints of reality: water drops that vibrate, flames that oscillate, and viscous fluids that form rivulets ...
<< In one of this year’s three winning videos, a drop of blue-dyed water at the bottom of an anise-oil and alcohol mixture begins to grow and shake, eventually pinching off a fragment that floats up. The process repeats several times. Created by now four-time Gallery-of-Fluid-Motion winner Oscar Enríquez of Carlos III University of Madrid and his colleagues, the visuals are accompanied by a soundtrack featuring a musical improvisation by a trio consisting of Enríquez on percussion, a violinist, and a clarinetist. Each instrument in the trio represents one of the three fluids. >>
Award-Winning Fluid Videos. APS. Physics 11, 121. Nov 21, 2018.