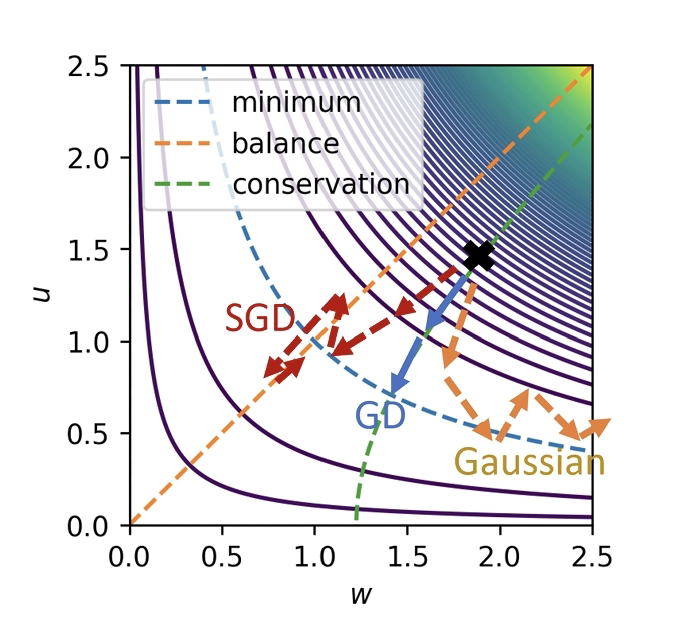
<< The stochastic gradient descent (SGD) algorithm is the algorithm (is used) to train neural networks. However, it remains poorly understood how the SGD navigates the highly nonlinear and degenerate loss landscape of a neural network. >>
<< In this work, (AA) show that the minibatch noise of SGD regularizes the solution towards a noise-balanced solution whenever the loss function contains a rescaling parameter symmetry. Because the difference between a simple diffusion process and SGD dynamics is the most significant when symmetries are present, (AA) theory implies that the loss function symmetries constitute an essential probe of how SGD works. (They) then apply this result to derive the stationary distribution of stochastic gradient flow for a diagonal linear network with arbitrary depth and width. >>
<< The stationary distribution exhibits complicated nonlinear phenomena such as phase transitions, broken ergodicity, and fluctuation inversion. These phenomena are shown to exist uniquely in deep networks, implying a fundamental difference between deep and shallow models. >>
Liu Ziyin, Hongchao Li, Masahito Ueda. Noise balance and stationary distribution of stochastic gradient descent. Phys. Rev. E 111, 065303. Jun 6, 2025.
Also: ai (artificial intell) (bot), network, noise, disorder & fluctuations, in https://www.inkgmr.net/kwrds.html
Keywords: ai, artificial intelligence, noise, stochasticity, networks, neural networks, deep learning,stochastic gradient descent (SGD), transitions, phase transitions, broken ergodicity, fluctuation inversion