Translate
sabato 12 aprile 2025
# gst: chaotic and time-periodic edge states in square duct flow.
sabato 20 novembre 2021
# gst: predict the wetting of the wedge; why do the teapots always drip?
mercoledì 30 giugno 2021
# gst: weird Nature; randomly arranged nanowire networks seem to behave, at the edge of chaos, like cortical neuronal cultures
sabato 13 maggio 2023
# gst: the robustness of a edge spiking.
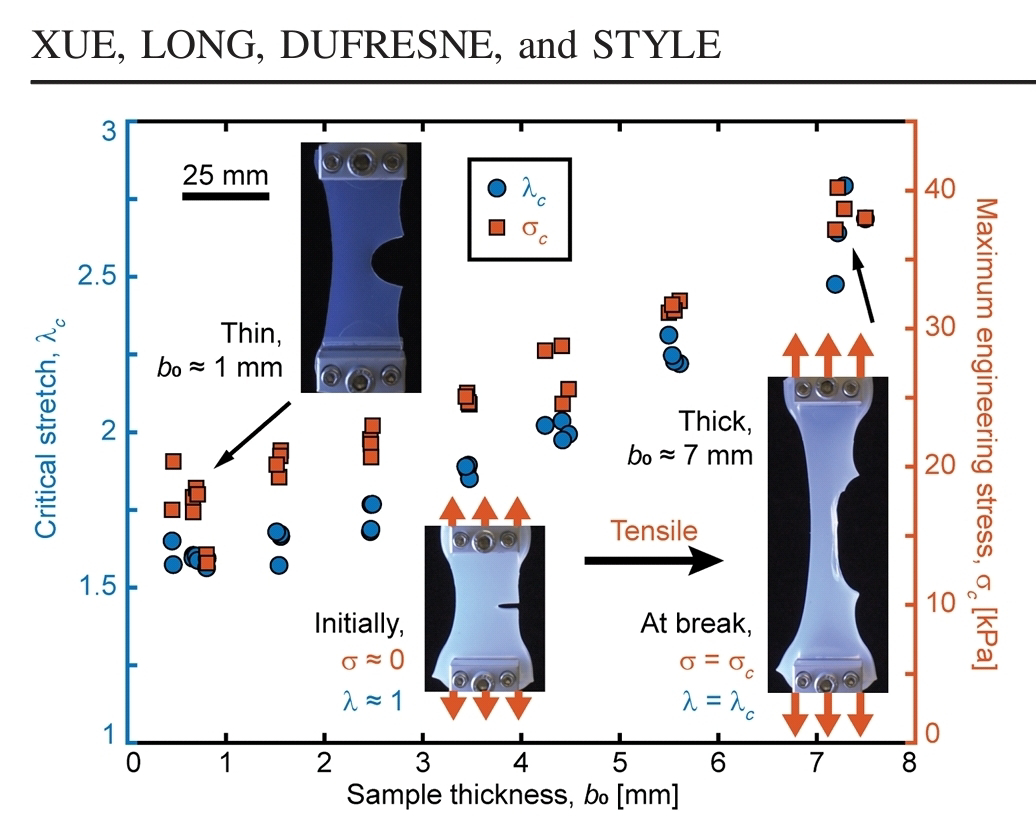
mercoledì 3 aprile 2024
# gst: elastomers fail from the edge.
sabato 21 agosto 2021
# gst: apropos of transitions, randomness can stabilize edge states in short- lifetime regions of disordered periodically-driven systems
martedì 28 gennaio 2025
# gst: tuning to the edge of instability (in the cochlea)
martedì 22 dicembre 2020
# gst: disorder can induce and modulate topological structures
mercoledì 20 settembre 2023
# gst: apropos of collisions of a vortex dipoles, vortex unbinding, vortex pinning to the edge, and emission of rarefaction pulses.
giovedì 20 febbraio 2025
# gst: friction-induced bubble edge curvature in flowing 2D confined foams
venerdì 1 dicembre 2023
# life: POTUS race 2024, Native voters could make a difference
giovedì 15 luglio 2021
# gst: apropos of turbulence, self-similarity of turbulent flows with internal and external intermittency
sabato 26 agosto 2017
# gst: modeling around the edge of a crack
<< It is said that a weak link determines the strength of the entire chain. Likewise, defects or small cracks in a solid material may ultimately determine the strength of that material – how well it will withstand various forces >>
<< What, exactly, happens right around the edge of the crack, in the area in which those large stresses are concentrated? >>
The Breaking Point. What happens at the moving edge of crack? Aug 23, 2017
https://wis-wander.weizmann.ac.il/chemistry/breaking-point
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/08/170823094054.htm
AA << show that cracks undergo an oscillatory instability controlled by small-scale, near crack-tip, elastic nonlinearity. This instability occurs above an ultrahigh critical velocity and features an intrinsic wavelength proportional to the ratio of the fracture energy to the elastic modulus (..) This ratio emerges as a fundamental scaling length assumed to play no role in the classical theory of cracks, but shown here to strongly influence crack dynamics >>
Chih-Hung Chen, Eran Bouchbinder & Alain Karma. Instability in dynamic fracture and the failure of the classical theory of cracks. Nature Physics doi: 10.1038/nphys4237 Publ. Aug 21, 2017
https://www.nature.com/nphys/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nphys4237.html
giovedì 22 luglio 2021
# life: transitions in the edges; to stimulate a shift in thinking, target small groups of people in the "outer edge" or fringe of a network.
mercoledì 12 marzo 2025
# gst: tandem droplets accelerated by continuous uniform airflow.
venerdì 6 dicembre 2024
# gst: anomalous oscillation modes of (superfluid) pendant droplets; horizontal translation on a flat surface, bouncing off at the corner and vertical oscillations at the edge.
domenica 26 ottobre 2025
# gst: transition to chaos with conical billiards.
sabato 8 novembre 2025
# gst: apropos of shape transitions, midveins regulate the shape formation of drying leaves.
sabato 9 marzo 2019
# behav: how to gain a competitive advantage over larger rivals by teaming up with another species (among the beetles Nicrophorus vespilloides)
AA << report that conflict within burying beetles Nicrophorus vespilloides influences the fitness that can be gained from interacting with the mite Poecilochirus carabi. Beetles transport these mites to carrion, upon which both species breed. >>
Syuan‐Jyun Sun, Nicholas P.C. Horrocks, Rebecca M. Kilner. Conflict within species determines the value of a mutualism between species. Evolution Letters. Mar 6, 2019. doi: 10.1002/evl3.109.
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/evl3.109
<< In a study featuring a miniature 'gym' for beetles (complete with beetle treadmills), [AA] found that beetles who consistently lose out to members of their own species have the most to gain by forming a mutually-beneficial cross-species partnership. >>
Mighty mites give scrawny beetles the edge over bigger rivals. University of Cambridge. Mar 5, 2019.
https://m.phys.org/news/2019-03-mighty-mites-scrawny-beetles-edge.html